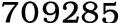|
1,4 Butanediol (CAS.NO:110-63-4) is a colorless liquid. It has a variety of applications in industry, as well as a psychoactive effect if ingested. Butanediol is rapidly converted into GHB via the alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes. 1.Uses 1,4-Butanediol is used as a GHB prodrug. Some users note that the high feels more "toxic" than GHB but still many users prefer the effect of 1,4-Butanediol over GHB. It is speculated that this is because 1,4-Butanediol has an effect on alcohol receptors in the brain even before it is converted into GHB. 2.Benefits and Applications 1,4-Butanediol is a versatile chemical intermediate because of its terminal, primary hydroxyl groups and its hydrophobic and chemical resistant nature. Polymers produced upon reaction with diacids or diisocyanates are the basis for many commercial polyurethane and polyester applications. Thermoplastic Polyesters. 1,4-Butanediol is used to manufacture polybutylene terephthalate (PBT). PBT's high strength, excellent thermal stability and good durability lead to its many uses in the automotive, electrical and appliance industries. PBT is also compatible with several other thermoplastics with several other thermoplastics which enables a compounder to tailor a polymer alloy to an end user's specifications. 3.Effects 1,4-Butanediol can lower a user's inhibitions. It causes euphoria and has aphrodesiac effects. An overdose can result in depressed breathing, a coma-like state. If combined with other CNS depressants, it can result in death. 4.Dangers 1,4 Butanediol is addictive in a similar manner to GHB. User reports suggest that it is more addictive. As previously stated avoid overdose or combination with cns depressants, which can result in loss of consciousness, depressed breathing and death.
Related Articles -
1, 4-Butanediol, 110-63-4,
|