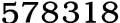|
Paclobutrazol (PBZ) is a plant growth retardant and triazole fungicide. It is a known antagonist of the plant hormone gibberellin. It acts by inhibiting gibberellin biosynthesis, reducing internodial growth to give stouter stems, increasing root growth, causing early fruitset and increasing seedset in plants such as tomato and pepper. PBZ has also been shown to reduce frost sensitivity in plants. Paclobutrazol(CAS NO:76738-62-0) is normally applied to the soil to be taken up by the roots and transported via the xylem to the upper parts of the plant. Foliar application is mostly ineffective. Seeds can be soaked with PBZ to reduce seedling growth. Paclobutrazol is used by arborists to reduce shoot growth and has been shown to have additional positive effects on trees and shrubs. Among those are improved resistance to drought stress, darker green leaves, higher resistance against fungi and bacteria, and enhanced development of roots. Cambial growth, as well as shoot growth, has been shown to be reduced in some tree species. A wide range of paclobutrazol concentrations are used on floriculture crops. Factors that influence appropriate rates include the crop, the magnitude of the response desired, crop maturity, volume of application and growing climate. A paclobutrazol spray at 5 to 10 ppm can be appropriate for bedding plants with moderate vigor, whereas at least twice that may be needed for aggressive crops, especially when grown during the late spring. On aggressive herbaceous perennials, typical spray rates are 60 to 90 ppm. None of the products can legally be applied to vegetable or herb crops. Paclobutrazol can be used as a sprench or drench when a longer-lasting response is desired. Some growers have success using multiple sprench applications, applied, for example, every few weeks, where the rates are adjusted based on the size and vigor of the crop. Another approach is to apply a drench at a high rate once the crop reaches a desirable size. However, late drenches are usually not recommended because the growth-inhibiting effect can continue after plants are planted into the landscape. A late drench may be appropriate for crops that are meant to remain in their containers, such as hanging baskets and potted flowering plants. For aggressive crops, early paclobutrazol applications are desirable once roots have reached the pot edges, typically seven to 10 days after transplant. Late applications of paclobutrazol, particularly when delivered as a spray, can delay flower development and reduce flower size. Therefore, early and proactive applications are strongly recommended, and late applications should generally be used as a last resort. Growers are encouraged to perform their own trials to determine appropriate rates for their growing conditions and specific crops. The product labels contain a lot of useful information, and extension educators and product technical managers can be consulted for application recommendations. To view photos of paclobutrazol applied to a range of bedding plants and herbaceous perennials, visit guidechem.com. Frankie is the freelance writer for e-commerce website in the chemistry. Guidechem.com is just a place for you to look for some chemicals. Our guidechem provide the most convenient conditions for the international buyers and let these leads benefit all the business people. Guidechem chemical B2B network provides information on china and global chemical market quotation and relative chemical Information. Guidechem Chemical Network providing the most complete information of the chemical industry.
Related Articles -
Paclobutrazol, guidechem, 76738-62-0,
|